In 2008 Princeton researchers demonstrated that sugar can be addictive. According to the study, sugar has the same effect on the brain as several over addictive drugs (1). The study concludes that rats meet 3/3 requirements for addiction: changes in behavior patterns that lead to increase intake of sugar, withdrawal, and craving and relapse.
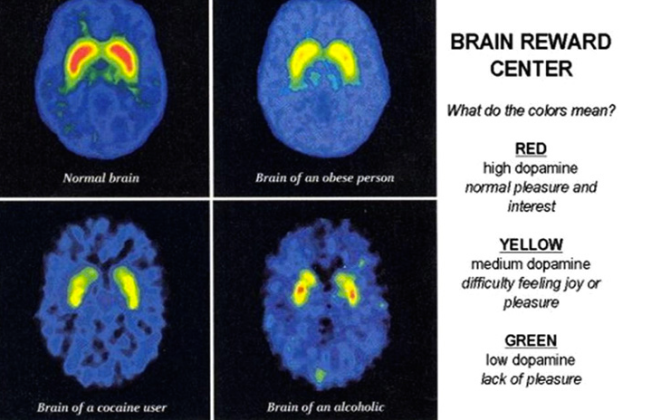
In 2012, Robert Lustig et al. published an article entitled, “Public Health: The toxic truth about sugar,” that produced evidence supporting the claim that sugar is addictive. According to MRIs and PETs, sugar, alcohol and cocaine are addictive substances that triggers dopamine, which acts on the nucleus accumbens, the pleasure and reward center of the brain (2).
The New Hampshire Department of Human Health Services produced a report that claims Americans eat an average of 152 pounds of sugar per year (3). This is because, as it was stated in Key Player: The Food Industry, a majority of our food items are laden with sugar. We are often unaware of the large amounts of sugar in most of our food items, even the food items that we feed to the youngest members of our society- our babies (4). The food that a pregnant women eats impacts the nutrient quality of the food her baby gets. Additionally, baby formula is packed with several grams of sugar alongside the other nutrients it provides. It is possible to assume that this overconsumption of sugar and addiction are cyclically linked.
Citation
- Hoebel, B. G., Avena, N., & Rada, P. Evidence For Sugar Addiction: Behavioral And Neurochemical Effects Of Intermittent, Excessive Sugar Intake. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 32, 20-39. Retrieved May 16, 2014.
- Brindis, C. D., Schmidt, L., & Lustig, R. Public health: The toxic truth about sugar. Nature,482, 27-29. Retrieved May 16, 2014.
- New Hampshire Department of Human Health Services. (2012). How much sugar do you eat? You may be surprised! Retrieved May 14, 2014.
- Bailin, D., Goldman, G., Phartiyal, P.. (May 2014) Sugar-coating science: How the Food industry misleads consumers on sugar. Center for Science and Democracy and Concerned Scientists. Retrieved May 13, 2014.
- Brain scan image. Retrieved from http://www.thinwomanbrain.com/images/food-addicts-big.jpg
- Sugar addiction diagram image. Retrieved from https://fbcdn-sphotos-a-a.akamaihd.net/hphotos-ak-ash4/420205_516208198421314_1965202903_n.png
- Sugar addiction header image. Retrieved from http://www.loveyourselflean.com/blog/2013/09/beat-your-sugar-addition-with-these-3-simple-steps/


Pingback: Alcoholism – INTRO (#1a) | HEAL & GROW for ACoAs